Fighting Varroa Destructor Through Science-Based Breeding
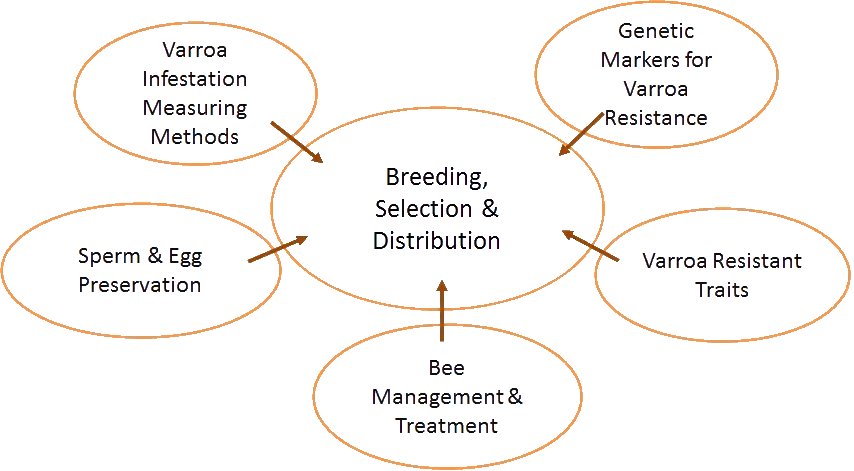
The Varroa Resistance Breeding & Selection Program (VRBSP) is Arista Bee Research’s flagship initiative to combat Varroa destructor mites—the leading cause of global honey bee colony losses. Based in the Netherlands and Belgium, our program combines advanced breeding, genetic research, and international collaboration to develop Varroa-resistant honey bee lines that support sustainable beekeeping across Europe, North America, and worldwide.